Difference between revisions of "Research"
From ACES
(Created page with "The ACES lab is conducting interdisciplinary research in robust ML, privacy-preserving technologies, automation and hardware, IP protection, and emerging technologies. == Rob...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Robust ML == | == Robust ML == | ||
Machine Learning (ML) models are often trained to satisfy a certain measure of performance such as classification accuracy, object detection accuracy, etc. In safety-sensitive tasks, a reliable ML model should satisfy reliability and robustness tests in addition to accuracy. Our group has made several key contributions to the development of robustness tests and safeguarding methodologies to enhance the reliability of ML systems. Some example projects are listed below: | Machine Learning (ML) models are often trained to satisfy a certain measure of performance such as classification accuracy, object detection accuracy, etc. In safety-sensitive tasks, a reliable ML model should satisfy reliability and robustness tests in addition to accuracy. Our group has made several key contributions to the development of robustness tests and safeguarding methodologies to enhance the reliability of ML systems. Some example projects are listed below: | ||
* Recent advances in adversarial Deep Learning (DL) have opened up a largely unexplored surface for malicious attacks jeopardizing the integrity of autonomous DL systems. With the wide-spread usage of DL in critical and time-sensitive applications, including unmanned vehicles, drones, and video surveillance systems, online detection of malicious inputs is of utmost importance. In a project called [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8587702 DeepFense], we propose the first end-to-end automated framework that simultaneously enables efficient and safe execution of DL models. DeepFense formalizes the goal of thwarting adversarial attacks as an optimization problem that minimizes the rarely observed regions in the latent feature space spanned by a DL network. To solve the aforementioned minimization problem, a set of complementary but disjoint modular redundancies are trained to validate the legitimacy of the input samples in parallel with the victim DL model. DeepFense leverages hardware/software/algorithm co-design and customized acceleration to achieve just-in-time performance in resource-constrained settings. The proposed countermeasure is unsupervised, meaning that no adversarial sample is leveraged to train modular redundancies. We further provide an accompanying API to reduce the non-recurring engineering cost and ensure automated adaptation to various platforms. Extensive evaluations on FPGAs and GPUs demonstrate up to two orders of magnitude performance improvement while enabling online adversarial sample detection.< | * Recent advances in adversarial Deep Learning (DL) have opened up a largely unexplored surface for malicious attacks jeopardizing the integrity of autonomous DL systems. With the wide-spread usage of DL in critical and time-sensitive applications, including unmanned vehicles, drones, and video surveillance systems, online detection of malicious inputs is of utmost importance. In a project called [https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8587702 DeepFense], we propose the first end-to-end automated framework that simultaneously enables efficient and safe execution of DL models. DeepFense formalizes the goal of thwarting adversarial attacks as an optimization problem that minimizes the rarely observed regions in the latent feature space spanned by a DL network. To solve the aforementioned minimization problem, a set of complementary but disjoint modular redundancies are trained to validate the legitimacy of the input samples in parallel with the victim DL model. DeepFense leverages hardware/software/algorithm co-design and customized acceleration to achieve just-in-time performance in resource-constrained settings. The proposed countermeasure is unsupervised, meaning that no adversarial sample is leveraged to train modular redundancies. We further provide an accompanying API to reduce the non-recurring engineering cost and ensure automated adaptation to various platforms. Extensive evaluations on FPGAs and GPUs demonstrate up to two orders of magnitude performance improvement while enabling online adversarial sample detection.<!-- | ||
[[File:Deepfense.png]] | --> [[File:Deepfense.png]] | ||
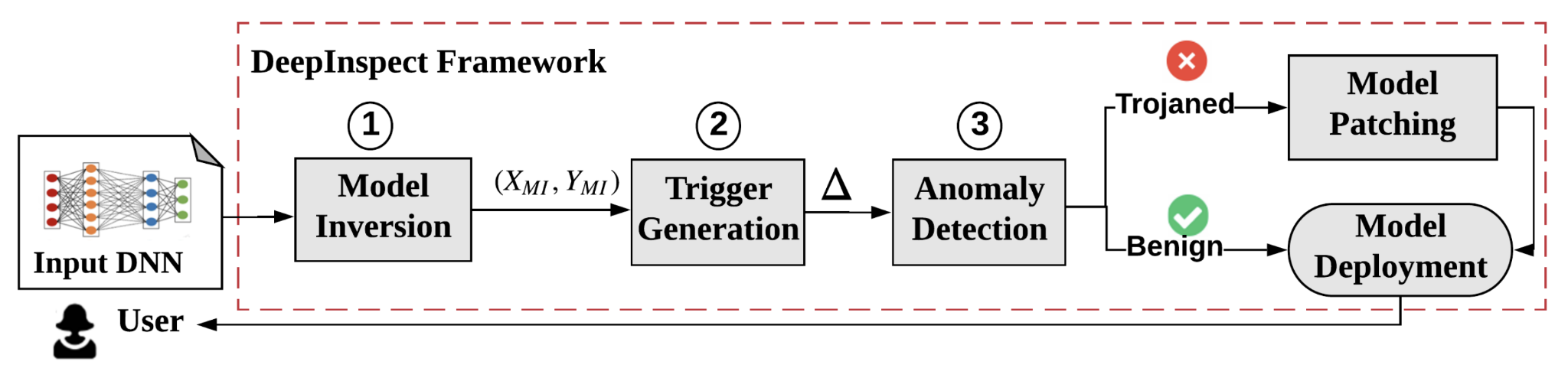
* Large-scale DL models are typically developed and trained by third-party companies that have sufficient computation power. These pre-trained models are then delivered to end users for real-world deployment. Such a supply chain raises security concerns about the pre-trained models obtained from untrusted parties. In our work DeepInspect, we propose the first black-box neural Trojan detection and mitigation framework that examines whether a given trained DL model has been backdoored during its training pipeline. DeepInspect leverages conditional GAN to emulate the backdoor attack and recovers potential Trojan triggers. We then use the footprint of the reconstructed triggers as the test metrics of hypothesis testing to determine the probability of Trojan insertion. In addition to reliable model-level Trojan detection, DeepInspect further enables the end users to improve model robustness by patching the pre-trained model with the perturbed inputs from the conditional generator with correct labels.<ref>huili please double check the text and add a picture</ref> | * Large-scale DL models are typically developed and trained by third-party companies that have sufficient computation power. These pre-trained models are then delivered to end users for real-world deployment. Such a supply chain raises security concerns about the pre-trained models obtained from untrusted parties. In our work DeepInspect, we propose the first black-box neural Trojan detection and mitigation framework that examines whether a given trained DL model has been backdoored during its training pipeline. DeepInspect leverages conditional GAN to emulate the backdoor attack and recovers potential Trojan triggers. We then use the footprint of the reconstructed triggers as the test metrics of hypothesis testing to determine the probability of Trojan insertion. In addition to reliable model-level Trojan detection, DeepInspect further enables the end users to improve model robustness by patching the pre-trained model with the perturbed inputs from the conditional generator with correct labels.<ref>huili please double check the text and add a picture</ref><!-- | ||
* Adversarial Deepfakes: Recent advances in video manipulation techniques have made the generation of fake videos more accessible than ever before. Manipulated videos can fuel disinformation and reduce trust in the media. Therefore detection of fake videos has garnered immense interest in academia and industry. Recently developed Deepfake detection methods rely on deep neural networks (DNNs) to distinguish AI-generated fake videos from real videos. In this work, we demonstrate that it is possible to bypass such detectors by adversarially modifying fake videos synthesized using existing Deepfake generation methods. We further demonstrate that our adversarial perturbations are robust to image and video compression codecs, making them a real-world threat. We present pipelines in both white-box and black-box attack scenarios that can fool DNN based Deepfake detectors into classifying fake videos as real.<ref>Shehzeen: please add a paragraph about adversarial attacks on Deepfakes and add a picture </ref> | --> [[File:DeepInspect Framework.png]] | ||
[[File:Adversarial Deepfakes.png]] | * Adversarial Deepfakes: Recent advances in video manipulation techniques have made the generation of fake videos more accessible than ever before. Manipulated videos can fuel disinformation and reduce trust in the media. Therefore detection of fake videos has garnered immense interest in academia and industry. Recently developed Deepfake detection methods rely on deep neural networks (DNNs) to distinguish AI-generated fake videos from real videos. In this work, we demonstrate that it is possible to bypass such detectors by adversarially modifying fake videos synthesized using existing Deepfake generation methods. We further demonstrate that our adversarial perturbations are robust to image and video compression codecs, making them a real-world threat. We present pipelines in both white-box and black-box attack scenarios that can fool DNN based Deepfake detectors into classifying fake videos as real.<ref>Shehzeen: please add a paragraph about adversarial attacks on Deepfakes and add a picture</ref><!-- | ||
--> [[File:Adversarial Deepfakes.png]] | |||
* Placeholder.<ref>Shehzeen: please add a paragraph about adversarial attacks and defense on Speech Recognition Models and add a picture</ref> | |||
* We also explore security threats and defense frameworks for Machine Learning models employed in audio/speech processing domains | * We also explore security threats and defense frameworks for Machine Learning models employed in audio/speech processing domains | ||
* Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Speech Recognition Systems: In this work, we demonstrate the existence of universal adversarial audio perturbations that cause mis-transcription of audio signals by automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. We propose an algorithm to find a single quasi-imperceptible perturbation, which when added to any arbitrary speech signal, will most likely fool the victim speech recognition model. Our experiments demonstrate the application of our proposed technique by crafting audio-agnostic universal perturbations for the state-of-the-art ASR system – Mozilla DeepSpeech. Additionally, we show that such perturbations generalize to a significant extent across models that are not available during training, by performing a transferability test on a WaveNet based ASR system. | * Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Speech Recognition Systems: In this work, we demonstrate the existence of universal adversarial audio perturbations that cause mis-transcription of audio signals by automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. We propose an algorithm to find a single quasi-imperceptible perturbation, which when added to any arbitrary speech signal, will most likely fool the victim speech recognition model. Our experiments demonstrate the application of our proposed technique by crafting audio-agnostic universal perturbations for the state-of-the-art ASR system – Mozilla DeepSpeech. Additionally, we show that such perturbations generalize to a significant extent across models that are not available during training, by performing a transferability test on a WaveNet based ASR system.<!-- | ||
[[File:Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Speech Recognition Systems.png]] | --> [[File:Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Speech Recognition Systems.png]] | ||
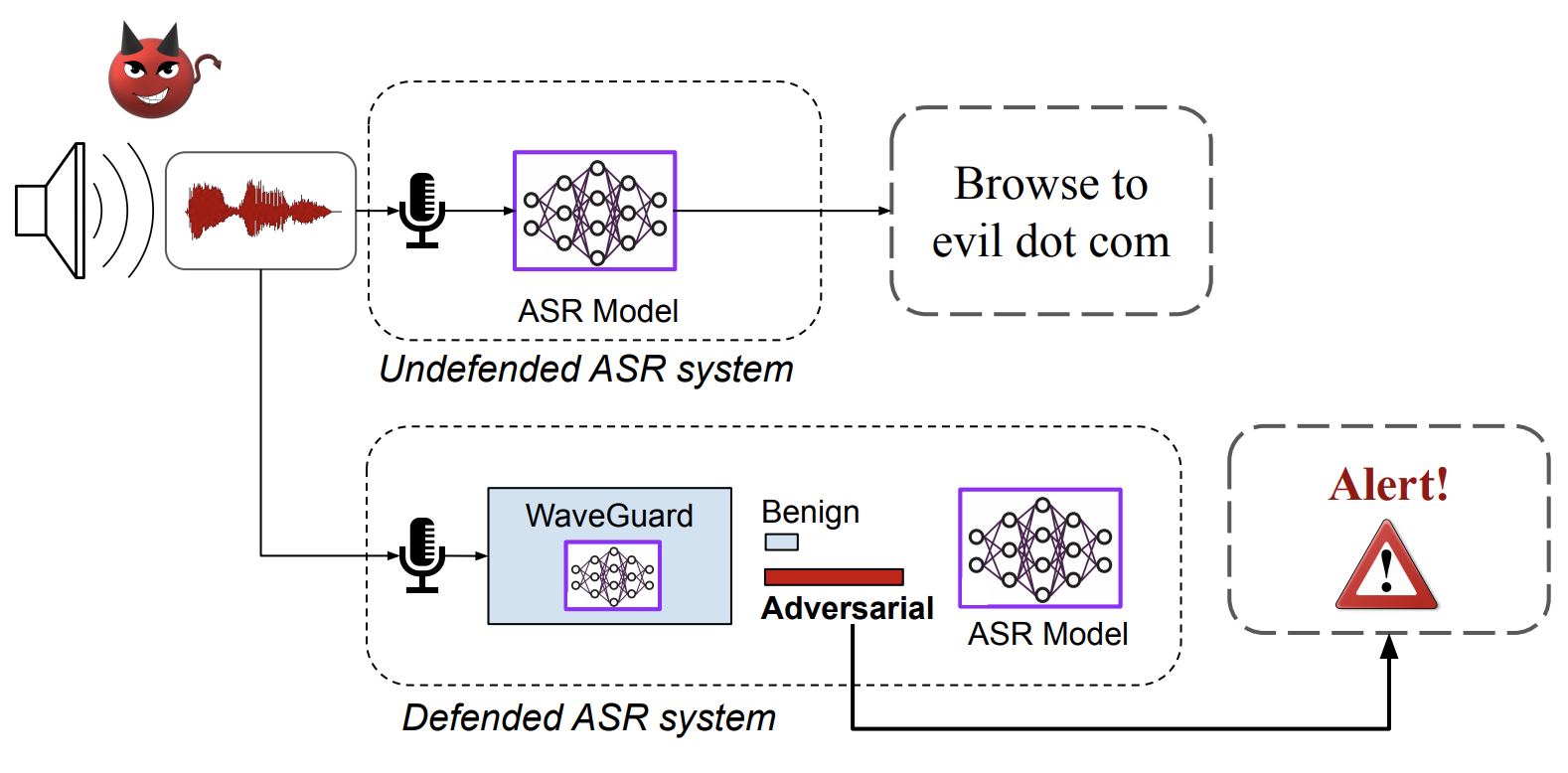
* Waveguard Defense Framework for Speech Recognition Systems: There has been a recent surge in adversarial attacks on deep learning based automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. These attacks pose new challenges to deep learning security and have raised significant concerns in deploying ASR systems in safety-critical applications. In this work, we introduce WaveGuard: a framework for detecting adversarial inputs that are crafted to attack ASR systems. Our framework incorporates audio transformation functions and analyses the ASR transcriptions of the original and transformed audio to detect adversarial inputs. We demonstrate that our defense framework is able to reliably detect adversarial examples constructed by four recent audio adversarial attacks, with a variety of audio transformation functions. With careful regard for best practices in defense evaluations, we analyze our proposed defense and its strength to withstand adaptive and robust attacks in the audio domain. We empirically demonstrate that audio transformations that recover audio from perceptually informed representations can lead to a strong defense that is robust against an adaptive adversary even in a complete white-box setting. Furthermore, WaveGuard can be used out-of-the box and integrated directly with any ASR model to efficiently detect audio adversarial examples, without the need for model retraining. | * Waveguard Defense Framework for Speech Recognition Systems: There has been a recent surge in adversarial attacks on deep learning based automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. These attacks pose new challenges to deep learning security and have raised significant concerns in deploying ASR systems in safety-critical applications. In this work, we introduce WaveGuard: a framework for detecting adversarial inputs that are crafted to attack ASR systems. Our framework incorporates audio transformation functions and analyses the ASR transcriptions of the original and transformed audio to detect adversarial inputs. We demonstrate that our defense framework is able to reliably detect adversarial examples constructed by four recent audio adversarial attacks, with a variety of audio transformation functions. With careful regard for best practices in defense evaluations, we analyze our proposed defense and its strength to withstand adaptive and robust attacks in the audio domain. We empirically demonstrate that audio transformations that recover audio from perceptually informed representations can lead to a strong defense that is robust against an adaptive adversary even in a complete white-box setting. Furthermore, WaveGuard can be used out-of-the box and integrated directly with any ASR model to efficiently detect audio adversarial examples, without the need for model retraining.<!-- | ||
[[File:Waveguard Defense Framework | --> [[File:Waveguard Defense Framework.png]] | ||
== Privacy-preserving technologies == | == Privacy-preserving technologies == | ||
Revision as of 23:07, 1 September 2021
The ACES lab is conducting interdisciplinary research in robust ML, privacy-preserving technologies, automation and hardware, IP protection, and emerging technologies.
Robust ML[edit | edit source]
Machine Learning (ML) models are often trained to satisfy a certain measure of performance such as classification accuracy, object detection accuracy, etc. In safety-sensitive tasks, a reliable ML model should satisfy reliability and robustness tests in addition to accuracy. Our group has made several key contributions to the development of robustness tests and safeguarding methodologies to enhance the reliability of ML systems. Some example projects are listed below:
- Recent advances in adversarial Deep Learning (DL) have opened up a largely unexplored surface for malicious attacks jeopardizing the integrity of autonomous DL systems. With the wide-spread usage of DL in critical and time-sensitive applications, including unmanned vehicles, drones, and video surveillance systems, online detection of malicious inputs is of utmost importance. In a project called DeepFense, we propose the first end-to-end automated framework that simultaneously enables efficient and safe execution of DL models. DeepFense formalizes the goal of thwarting adversarial attacks as an optimization problem that minimizes the rarely observed regions in the latent feature space spanned by a DL network. To solve the aforementioned minimization problem, a set of complementary but disjoint modular redundancies are trained to validate the legitimacy of the input samples in parallel with the victim DL model. DeepFense leverages hardware/software/algorithm co-design and customized acceleration to achieve just-in-time performance in resource-constrained settings. The proposed countermeasure is unsupervised, meaning that no adversarial sample is leveraged to train modular redundancies. We further provide an accompanying API to reduce the non-recurring engineering cost and ensure automated adaptation to various platforms. Extensive evaluations on FPGAs and GPUs demonstrate up to two orders of magnitude performance improvement while enabling online adversarial sample detection.

- Large-scale DL models are typically developed and trained by third-party companies that have sufficient computation power. These pre-trained models are then delivered to end users for real-world deployment. Such a supply chain raises security concerns about the pre-trained models obtained from untrusted parties. In our work DeepInspect, we propose the first black-box neural Trojan detection and mitigation framework that examines whether a given trained DL model has been backdoored during its training pipeline. DeepInspect leverages conditional GAN to emulate the backdoor attack and recovers potential Trojan triggers. We then use the footprint of the reconstructed triggers as the test metrics of hypothesis testing to determine the probability of Trojan insertion. In addition to reliable model-level Trojan detection, DeepInspect further enables the end users to improve model robustness by patching the pre-trained model with the perturbed inputs from the conditional generator with correct labels.[1]
- Adversarial Deepfakes: Recent advances in video manipulation techniques have made the generation of fake videos more accessible than ever before. Manipulated videos can fuel disinformation and reduce trust in the media. Therefore detection of fake videos has garnered immense interest in academia and industry. Recently developed Deepfake detection methods rely on deep neural networks (DNNs) to distinguish AI-generated fake videos from real videos. In this work, we demonstrate that it is possible to bypass such detectors by adversarially modifying fake videos synthesized using existing Deepfake generation methods. We further demonstrate that our adversarial perturbations are robust to image and video compression codecs, making them a real-world threat. We present pipelines in both white-box and black-box attack scenarios that can fool DNN based Deepfake detectors into classifying fake videos as real.[2]

- Placeholder.[3]
- We also explore security threats and defense frameworks for Machine Learning models employed in audio/speech processing domains
- Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Speech Recognition Systems: In this work, we demonstrate the existence of universal adversarial audio perturbations that cause mis-transcription of audio signals by automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. We propose an algorithm to find a single quasi-imperceptible perturbation, which when added to any arbitrary speech signal, will most likely fool the victim speech recognition model. Our experiments demonstrate the application of our proposed technique by crafting audio-agnostic universal perturbations for the state-of-the-art ASR system – Mozilla DeepSpeech. Additionally, we show that such perturbations generalize to a significant extent across models that are not available during training, by performing a transferability test on a WaveNet based ASR system.

- Waveguard Defense Framework for Speech Recognition Systems: There has been a recent surge in adversarial attacks on deep learning based automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. These attacks pose new challenges to deep learning security and have raised significant concerns in deploying ASR systems in safety-critical applications. In this work, we introduce WaveGuard: a framework for detecting adversarial inputs that are crafted to attack ASR systems. Our framework incorporates audio transformation functions and analyses the ASR transcriptions of the original and transformed audio to detect adversarial inputs. We demonstrate that our defense framework is able to reliably detect adversarial examples constructed by four recent audio adversarial attacks, with a variety of audio transformation functions. With careful regard for best practices in defense evaluations, we analyze our proposed defense and its strength to withstand adaptive and robust attacks in the audio domain. We empirically demonstrate that audio transformations that recover audio from perceptually informed representations can lead to a strong defense that is robust against an adaptive adversary even in a complete white-box setting. Furthermore, WaveGuard can be used out-of-the box and integrated directly with any ASR model to efficiently detect audio adversarial examples, without the need for model retraining.
Privacy-preserving technologies[edit | edit source]
As data-mining algorithms are being incorporated into today’s technology, concerns about data privacy are rising. The ACES Lab has been contributing to the field of privacy-preserving computing for more than a decade now, and it still remains one of the pioneers in the area. Several signature research domains of our group are listed below.
- Our group is dedicated to execution of Secure Function Evaluation (SFE) protocols in practical time limits. Along with algorithmic optimizations, we are working on acceleration of the inherent computation by designing application specific accelerators. FASE [FCCM'19], currently the fastest accelerator for the Yao's Garbled Circuit (GC) protocol is designed by the ACES Lab. It outperformed the previous works by a minimum of 110 times in terms of throughput per core. Our group also developed MAXelerator [DAC'18] - an FPGA accelerator for GC customized for matrix multiplication. It is 4 times faster than FASE for this particular operation. MAXelerator is one of the examples of co-optimizations of the algorithm and the underlying hardware platform. Our current projects include acceleration of Oblivious Transfer (OT) and Homomorphic Encryption (HE). Moreover, as part of our current efforts to develop practical privacy-preserving Federated Learning (FL), we are working on evaluation of the existing hardware cryptographic primitives on Intel processors and devising new hardware-based primitives that complement the available resources. Our group plans to design efficient systems through the co-optimization of the FL algorithms, defense mechanisms, cryptographic primitives, and the hardware primitives. [4]
- Advancements in deep neural networks have fueled machine learning as a service, where clients receive an inference service from a cloud server. Many applications such as medical diagnosis and financial data analysis require the client’s data to remain private. The objective of privacy-preserving inference is to use secure computation protocols to perform inference on the client’s data, without revealing the data to the server. Towards this goal, the ACES lab has been conducting exemplary research in the intersection DNN inference and secure computation. We have developed several projects including DeepSecure, Chameleon, XONN, SlimBin, COINN, and several on-going projects. The core idea of our work is to co-optimize machine learning algorithms with secure execution protocols to achieve a better tradeoff between accuracy and runtime. Using this co-optimization approach, our customized DNN inference solutions have achieved significant runtime improvements over contemporary work.
Automation and Hardware[edit | edit source]
- ↑ huili please double check the text and add a picture
- ↑ Shehzeen: please add a paragraph about adversarial attacks on Deepfakes and add a picture
- ↑ Shehzeen: please add a paragraph about adversarial attacks and defense on Speech Recognition Models and add a picture
- ↑ Siam: please add tinygarble and add a picture for all of the papers mentioned in this paragraph.